Latissimus Dorsi Muscle: Anatomy, Function, and Importance

Introduction
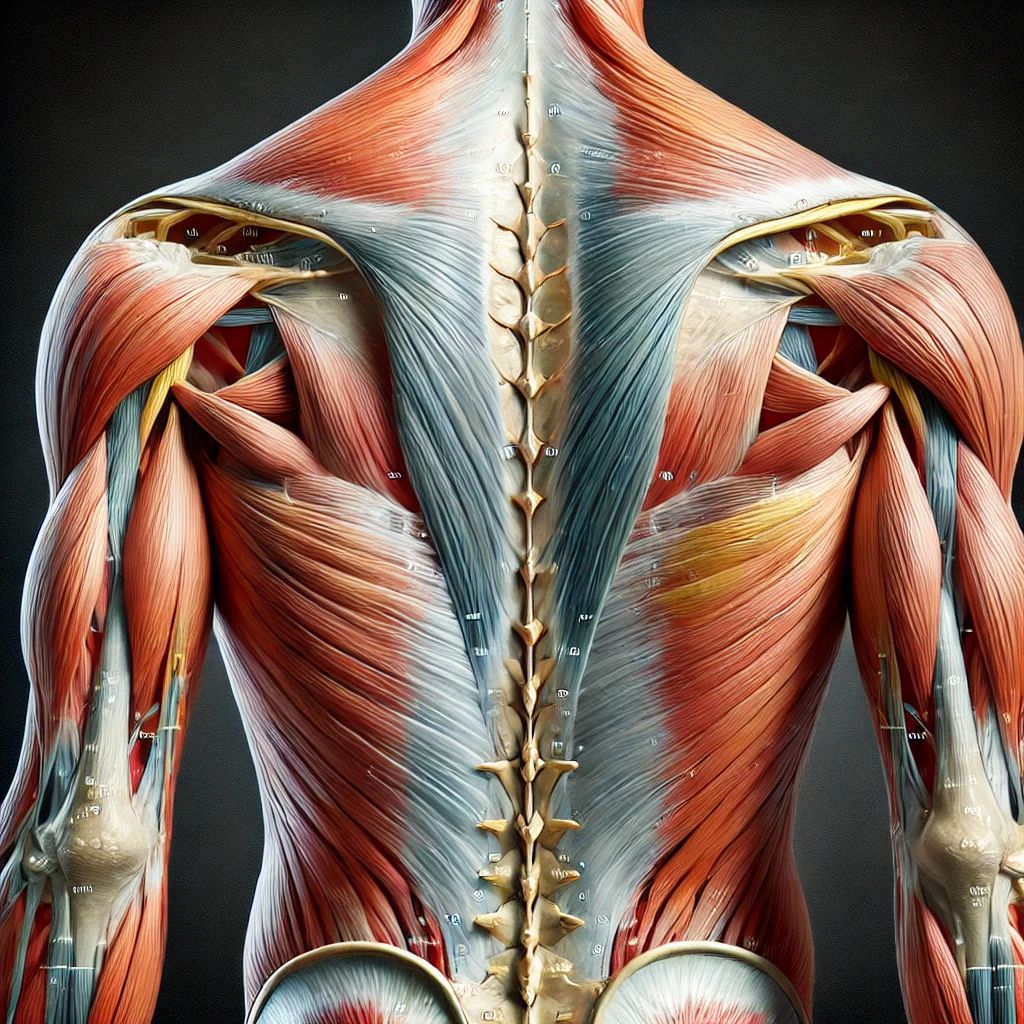
The latissimus dorsi, commonly referred to as the “lats,” is one of the largest muscles in the human body. It plays a crucial role in upper body movement, posture, and overall strength. This broad, flat muscle is located in the back and extends from the lower spine to the upper arm, contributing significantly to the V-shaped torso seen in athletes and bodybuilders.
Anatomy of the Latissimus Dorsi**
The latissimus dorsi originates from multiple points:
Thoracolumbar fascia (a connective tissue in the lower back)
Lower six thoracic vertebrae (T7-T12)
Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
Iliac crest (upper part of the pelvis)
Lower three or four ribs
Inferior angle of the scapula (in some cases)
It inserts into the intertubercular groove of the humerus, allowing it to influence shoulder movement. The muscle is innervated by the thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8), which originates from the brachial plexus.
Function of the Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi is responsible for several key movements, including:
1. Shoulder Adduction – Bringing the arm closer to the body, such as during pull-ups or swimming strokes.
2. Shoulder Extension– Moving the arm backwards, as in rowing or pulling motions.
3. Internal Rotation of the Shoulder – Rotating the arm inward.
4. Assisting in Respiration– The lats help with forced expiration during heavy breathing.
Importance in Daily Life and Sports
The latissimus dorsi plays a vital role in various physical activities:
– Sports – It is essential for swimmers, rowers, gymnasts, and weightlifters who rely on upper body strength.
– Posture and Stability – It supports proper posture by stabilizing the spine and shoulders.
Functional Movements– The lats assist in everyday activities like lifting, pulling, and reaching overhead.
Strengthening and Stretching the Latissimus Dorsi
Exercises to Strengthen the Lats
1. Pull-ups/Chin-ups– Excellent for building lat strength.
2. Lat Pulldowns – A machine-based exercise that targets the lats directly.
3. Bent-over Rows – Strengthens the lats along with other back muscles.
4. Deadlifts – Although a full-body exercise, deadlifts engage the lats for stabilization.
Stretching the Latissimus Dorsi
1. Overhead Lat Stretch– Raise one arm overhead and lean to the opposite side.
2. Child’s Pose Stretch_ Extend the arms forward while sitting back on the heels.
3. Wall Lat Stretch– Place hands on a wall and lean forward to stretch the lats.
Common Injuries and How to Prevent Them
Latissimus dorsi injuries are rare but can occur due to overuse, heavy lifting, or sudden trauma. Common issues include:
– Muscle Strains– Caused by overstretching or excessive force.
– Tendonitis – Inflammation due to repetitive motions.
Prevention Tips
– Warm up properly before workouts.
– Incorporate flexibility exercises to prevent stiffness.
– Avoid excessive weightlifting without proper form.
Conclusion
The latissimus dorsi is a powerful muscle that contributes to strength, mobility, and overall physical performance. Strengthening and stretching the lats can improve posture, enhance athletic performance, and prevent injuries. Whether you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or someone looking to improve functional movement, maintaining a strong and flexible latissimus dorsi is essential for overall health and well-being.
Dr.Nigahe Zahra Syed (PT)


